STAGES OF CONSTITUTION-MAKING
Welcome to this section where we'll take you through a stage-by-stage overview of how the Indian Constituent Assembly drafted the Constitution of India. We've provided you with links to primary and secondary resources to help you delve deeper. Be sure to check out our popular video on constitution-making!
First Session of the Constituent Assembly
On 13 December 1946, the Constituent Assembly formally commenced its task of framing the Constitution of India. Jawaharlal Nehru moved the Objectives Resolution, which aimed to declare India as an Independent Sovereign Republic and create a Constitution to govern its future. The Resolution established general principles to guide the work of the Constituent Assembly. On January 22, 1947, the Constituent Assembly adopted the Resolution.
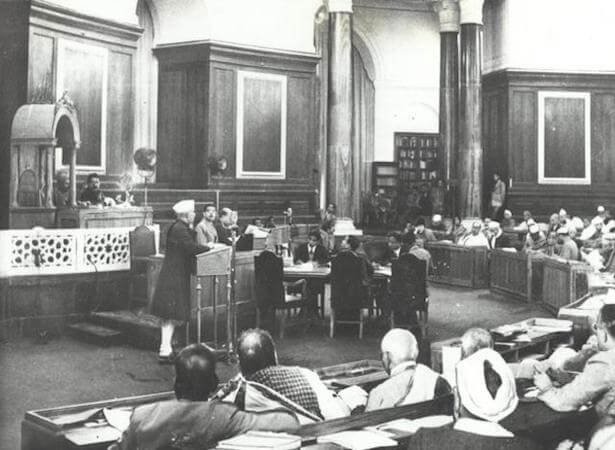

Committee Stages and Second Session of Constituent Assembly Debates
After the first session of the Constituent Assembly, several committees were established to examine and report on various aspects of the Constitution. These included the Advisory Committee on Fundamental Rights, Minorities, and Tribal and Excluded Areas (comprising the Sub-Committee on Fundamental Rights and the Sub-Committee on Minority Rights), Union Powers Committee, Union Constitution Committee, and Provincial Constitution Committee. These committees submitted their reports to the Constituent Assembly between April and August 1947. Meanwhile, as the committees submitted their reports, the Constituent Assembly discussed the general principles outlined in the recommendations. These deliberations concluded on 30 August 1947.
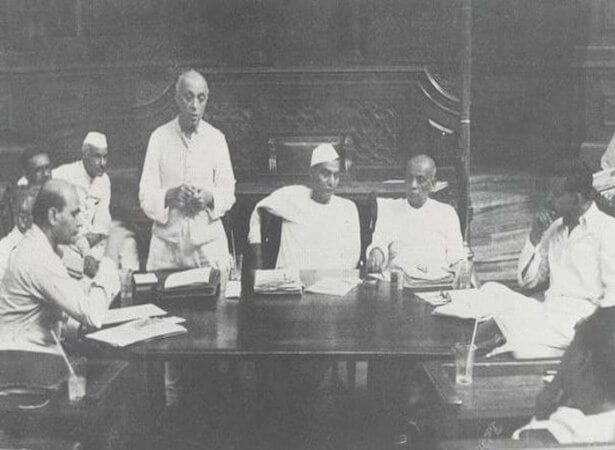

Draft Constitution by the Constitutional Adviser
Based on the reports of various committees and discussions in the Constituent Assembly mentioned in the previous stages, B.N. Rau, the Constitutional Adviser to the Constituent Assembly, prepared a Draft Constitution. The Draft Constitution was completed by October 1947 and submitted to the Drafting Committee.
First Draft Constitution
On 27 October 1947, the Drafting Committee began scrutinising the Draft Constitution prepared by the Constitutional Advisor, along with other notes, reports, and memoranda. After making changes, the committee submitted its final Draft Constitution to the President of the Constituent Assembly on 21 February 1948.

Public Circulation of Draft Constitution of India
After the Draft Constitution was submitted to the President of the Constituent Assembly, it was published and circulated among the public. Many comments, critiques, and suggestions were received, which were then scrutinized by a Special Committee comprising members of the Union Constitution Committee, Provincial Constitution Committee, Union Powers Committee, and the Drafting Committee itself. The Drafting Committee took these inputs into account and held discussions on 23, 24, 27 March and 18 October 1948. On 26 October 1948, the Committee reprinted and resubmitted the version of the Draft Constitution that had been submitted on February 21st, 1948, along with a set of amendments appended to clauses it intended to amend.

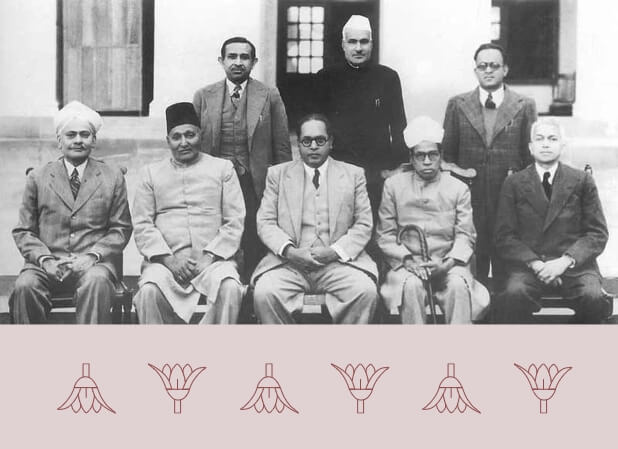
Draft Constitution Presented to the Constituent Assembly
The Draft Constitution was presented to the Constituent Assembly on 4 November 1948, by B.R. Ambedkar, the Chairman of the Drafting Committee. This version of the Draft Constitution was submitted to the President of the Constituent Assembly in February 1948, along with a list of suggested amendments that emerged from the scrutiny of comments received from stakeholders and the general public. The Draft Constitution was now opened up for discussion in the Assembly.

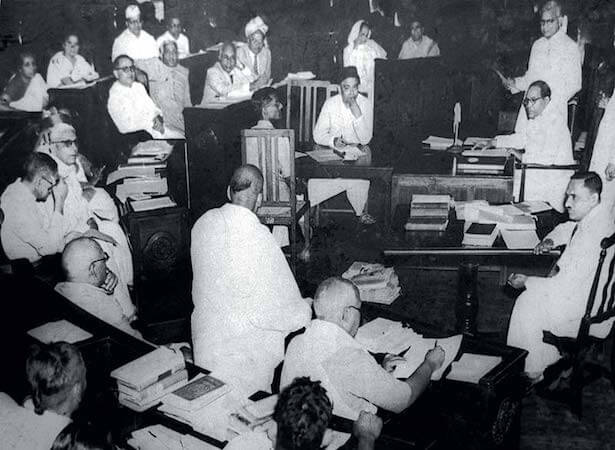
First Reading of the Draft Constitution
In the First Reading of the Draft Constitution, the Constituent Assembly engaged in a clause-by-clause discussion of every Article in the Draft Constitution. Most significant and extensive debates of the Constituent Assembly occurred during this period, which lasted until 17 October 1949. During this stage, Assembly members frequently proposed amendments to the Draft Constitution, seeking to modify or eliminate specific articles or clauses. But the majority of amendments were ultimately rejected.
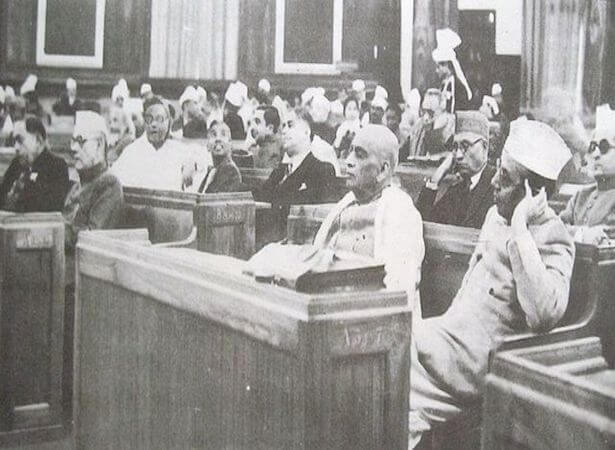

Revision and Second Reading of the Draft Constitution
After the debates surrounding the Draft Constitution concluded, the Drafting Committee proceeded to revise it in accordance with decisions made in the Constituent Assembly. This involved tasks such as renumbering articles, making minor changes to the language, and adding or removing clauses. The revised Draft Constitution was then submitted to the President of the Constituent Assembly on 3 November 1949. It was subsequently introduced in the Assembly on 14 November 1949.

Third Reading of Drafting Constitution
During the third reading of the Draft Constitution there were only a few significant debates, and most of the speeches consisted of general comments on the Constitution as a whole. While some members expressed satisfaction with the final version of the Constitution, others raised concerns.

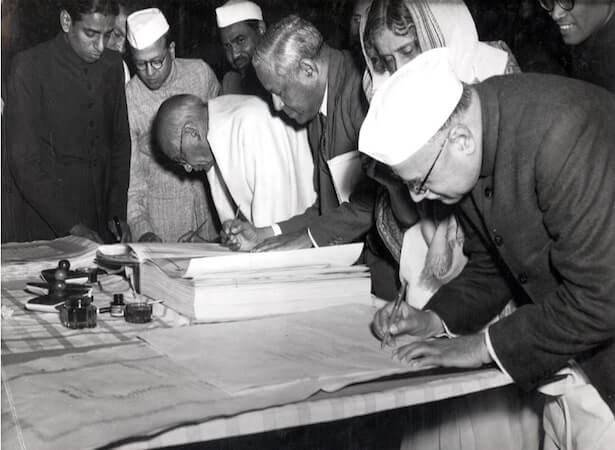
Enactment and Adoption of the Constitution of India
On 26 November 1949, the third reading of the Constitution came to an end with the Constituent Assembly voting in favour of the motion proposed by Ambedkar in the previous stage. The final version of the Constitution was signed by members of the Assembly on 24 January 1950, and it came into effect on 26 January 1950.

